Tauro Collar Data Format
Once SD cards have been recovered from a deployment and the raw binary files decoded into CSV’s using the Tauro Data Decoder, the next step is analysing the data. The purpose of this document is to list the possible output files and their contents. There are two broad classes of data logged to the SD card. The first is data generated locally on the Tauro Research Collar. The second is data logged from a paired Ceres Ear Tag.
Contents
Tauro Locally Generated Data
The Tauro Collar generates a number of different data files, each with a specific purpose. The files are named using the following convention:
infuse_{id}_{data_type}.csv
Where {id} is the unique identifier for the Tauro Collar device, and {data_type} indicates the type of data contained in the file. The possible data types are described below.
1. Accelerometer Data {infuse_{id}_ACC_4G.csv}
Raw accelerometer samples from the Bosch BMI270 6-axis IMU1. The IMU samples at 60Hz, giving an expected period between samples of approximately 16.67 milliseconds (or 16667 microseconds).
time,x,y,z
2025-01-23T01:44:03.000000Z,2858,-2215,9335
2025-01-23T01:44:03.016036Z,1569,-151,8000
2025-01-23T01:44:03.032073Z,2667,-291,8939
2025-01-23T01:44:03.048110Z,2347,-1963,9606
The data is recorded in its raw format directly from the accelerometer, not converted into G’s. A maximum value of 32768 corresponding to an acceleration of +4G on that axis. As an example, converting the raw value of 8000 from the Z axis in the first row of the sample.
acceleration_g = 4 * 8000 / 32768
= 0.976
The following section from the datasheet describes the individual axes and the expected data readings in various orientations.
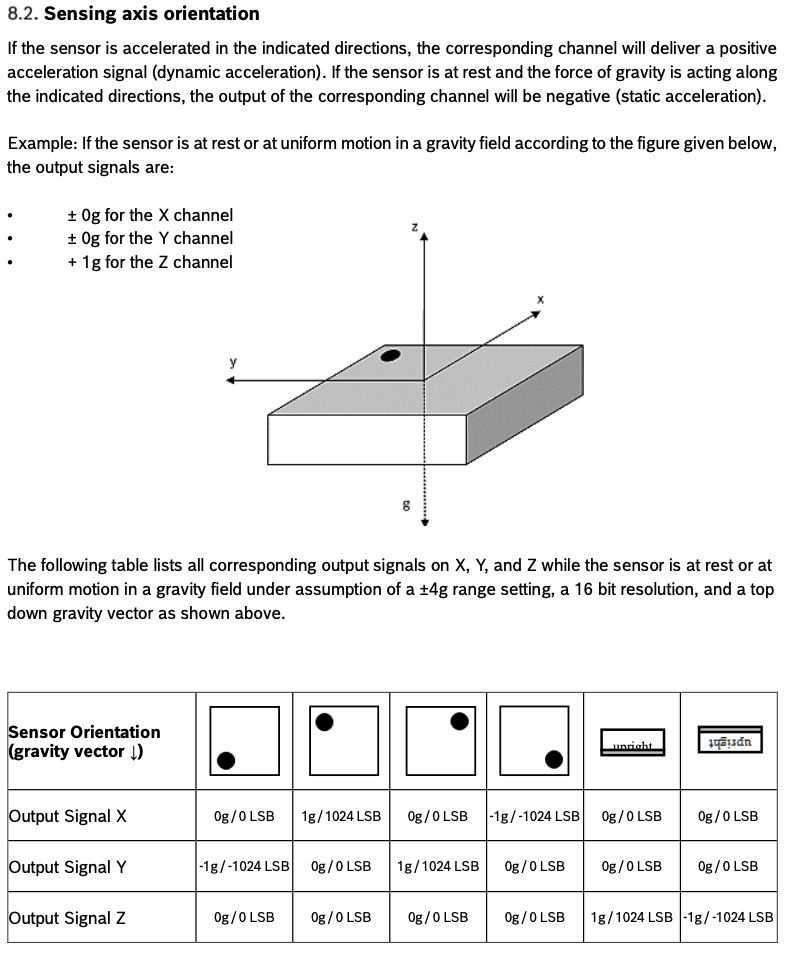
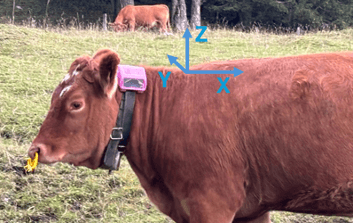
When the collar is on the animal, the orientation of the axes will be as follows:
2. Gyroscope Data {infuse_{id}_GYR_500DPS.csv}
Raw gyroscope samples from the Bosch BMI270 6-axis IMU. The gyroscope samples at 60Hz, giving an expected period between samples of approximately 16.67 milliseconds (or 16667 microseconds).
time,x,y,z
2025-01-23T01:44:03.000000Z,420,-78,-740
2025-01-23T01:44:03.016036Z,101,24,-574
2025-01-23T01:44:03.032073Z,-195,-9,-472
2025-01-23T01:44:03.048110Z,-649,277,-371
The axes match those from the accelerometer described above, with a maximum value of 32768 corresponding to a rotation of 250 degrees per second around that axis. As an example, converting the raw value of -740 from the Z axis in the first row of the sample.
degrees_per_second = 250 * -740 / 32768
= -5.646
The gyroscope is sampled on the same internal timer as the accelerometer, meaning that both files should have samples at the same timestamps.
3. GNSS Location Data {infuse_{id}_UBX_NAV_PVT.csv}
Complete NAV-PVT frames from the Ublox M10 GNSS modem2 that is configured to output a NAV-PVT frame once every second, so this file will contain a 1Hz log of location data.
time,itow,year,month,day,hour,min,sec,valid,t_acc,nano,fix_type,flags,flags2,num_sv,lon,lat,height,h_msl,h_acc,v_acc,vel_n,vel_e,vel_d,g_speed,head_mot,s_acc,head_acc,p_dop,flags3,reserved0[0],reserved0[1],reserved0[2],reserved0[3],head_veh,mag_dec,mag_acc
2025-01-23T01:44:03.028778Z,351861000,2025,1,23,1,44,3,0x37,29,-10779,3,0x01,0xea,26,152.4564233,-27.7402103,133.188,95.348,2.432,4.347,16.759,13.633,0.139,21.604,39.12696,0.181,0.32176,1.1,0x0000,92,64,86,47,0,0,0
2025-01-23T01:44:04.028900Z,351862000,2025,1,23,1,44,4,0x37,29,-10225,3,0x01,0xea,27,152.4565731,-27.7400736,132.962,95.122,2.401,4.233,14.43,15.377,0.057,21.087,46.81985,0.258,0.58152,1.1,0x0000,92,64,86,47,0,0,0
2025-01-23T01:44:05.028900Z,351863000,2025,1,23,1,44,5,0x37,28,-9671,3,0x01,0xea,26,152.4567458,-27.739961,133.279,95.439,2.372,4.107,11.648,17.667,-0.309,21.161,56.6028,0.183,0.34996,1.07,0x0000,92,64,86,47,0,0,0
This file contains a 1Hz log of all the location information output by the GNSS modem. The complete definition of every field can be found at section 3.15.9 (UBX-NAV-PVT) in the M10 interface description. Some conversions are applied to the raw data to switch to base SI units (for example from millimeters to meters). As a brief summary of each field:
| Field | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| iTOW | GPS time of week of the navigation epoch | |
| year | UTC year | |
| month | UTC month | |
| day | UTC day | |
| hour | UTC hour | |
| min | UTC minute | |
| sec | UTC second | |
| valid | Time validity flags | |
| t_acc | Nanoseconds | Time accuracy estimate |
| nano | Nanoseconds | UTC fraction of second |
| fixType | Strength of the GNSS location fix | |
| flags | Flags relating to the GNSS location fix | |
| flags2 | Additional time validity flags | |
| numSV | Number of satellites used in the location fix | |
| lon | Degrees | Longitude |
| lat | Degrees | Latitude |
| height | Meters | Height about the WGS84 ellipsoid |
| hMSL | Meters | Height above mean sea level |
| hACC | Meters | Horizontal accuracy estimate |
| vAcc | Meters | Vertical accuracy estimate |
| velN | Meters/second | North-East-Down velocity in North direction |
| velE | Meters/second | North-East-Down velocity in East direction |
| velD | Meters/second | North-East-Down velocity in Down direction |
| gSpeed | Meters/second | Ground speed (2D) |
| headMot | Degrees | Heading of motion (2D) |
| sAcc | Meters/second | Speed accuracy |
| headAcc | Degrees | Heading accuracy |
| pDOP | Position Dilution-of-Precision | |
| flags3 | Extra flags | |
| headVeh | Degrees | Heading of vehicle (2D) (Unused) |
| magDec | Degrees | Magnetic declination (Unused) |
| magAcc | Degrees | Magnetic declination accuracy (Unused) |
4. Battery and Power Data {infuse_{id}_BATTERY_STATE.csv}
Log of battery voltage and current measurements, as well as solar charging current.
time,voltage_mv,current_ua,soc
2025-01-23T01:44:07.997833Z,3902,0,86
2025-01-23T01:44:12.997833Z,3902,0,86
2025-01-23T01:44:17.997833Z,3902,0,86
2025-01-23T01:44:22.997589Z,3902,0,86
The battery data is logged at a 5 second interval, with each row containing the following fields:
| Field | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| voltage_mv | Millivolts | Measured battery voltage |
| current_ua | Microamps | Measured battery current (positive when discharging, negative when charging) |
| soc | Percentage | Estimated state of charge of the battery |
5. Ambient Environment Data {infuse_{id}_AMBIENT_TEMP_PRES_HUM.csv}
Log of ambient temperature, pressure, and humidity measurements from the Bosch BME680 sensor.
time,temperature,pressure,humidity
2025-01-23T01:44:08.073089Z,39.74,99.754,49.65
2025-01-23T01:44:13.073089Z,39.71,99.725,49.64
2025-01-23T01:44:18.073089Z,39.68,99.74,49.69
2025-01-23T01:44:24.669616Z,39.67,99.749,49.67
The ambient environment data is logged at a 5 second interval, with each row containing the following fields:
| Field | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| time | UTC Timestamp. | Timestamp of the measurement |
| temperature | Degrees | Ambient temperature |
| pressure | Kilopascals (kPa) | Ambient pressure |
| humidity | Relative Humidity | Ambient humidity |
6. CSIRO eGrazor Data {infuse_{id}_ALGORITHM_OUTPUT.csv}
Log of activity classification data generated by the CSIRO eGrazor algorithm3 running on the Tauro Collar. The algorithm processes accelerometer data in real-time and outputs a classified activity state every 5 seconds.
time,algorithm_id,algorithm_version,output
2025-01-23T01:44:03.192504Z,0xce7e5002,2,04
2025-01-23T01:44:08.326416Z,0xce7e5002,2,04
2025-01-23T01:44:13.460296Z,0xce7e5002,2,04
2025-01-23T01:44:18.594177Z,0xce7e5002,2,04
The output is an enumerated value representing the classified activity state of the animal. The possible output values are:
| Output Value | Output Class |
|---|---|
| 00 | Grazing |
| 01 | Walking |
| 02 | Ruminating |
| 03 | Resting |
| 04 | Drinking |
| 05 | Other |
7. Time Synchronization Data {infuse_{id}_TIME_SYNC.csv}
The Tauro research collar periodically (typically once an hour) updates into local time knowledge either from the GNSS modem or over the LTE network via SNTP. This is done because the local crystal oscillators are not perfect and will drift over time.
time,source,shift
2025-01-23T01:59:36.122985Z,1,-0.053864
2025-01-23T02:59:37.114944Z,1,-0.090836
2025-01-23T03:59:38.119171Z,1,-0.112442
The time source field indicates where the time update was obtained from:
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | GNSS |
| 1 | NTP (Over LTE) |
The data in this file can be used to view the average drift over time and correct for jumps in the timestamps in other files, if desired. For this file, the time column represents the current time after being synchronised, while the shift column is the number of seconds that were skipped. A negative value means the local time knowledge jumped backwards.
8. Companion Ear Tag BLE Connection {infuse_{id}_BLUETOOTH_CONNECTION.csv}
Log of Bluetooth connection events with a paired Companion Ear Tag.
time,type,val,connected
2025-01-23T04:33:38.469146Z,0,0x60fcf10031da,1
2025-01-23T04:35:17.073730Z,0,0x60fcf10031da,0
2025-01-23T04:35:44.144958Z,0,0x60fcf10031da,1
2025-01-23T04:44:35.153106Z,0,0x60fcf10031da,0
The Bluetooth connection data is logged whenever a connection or disconnection event occurs with a paired Companion Ear Tag.
9. Companion Ear Tag Bluetooth RSSI: {infuse_{id}_BLUETOOTH_RSSI.csv}
If paired to a Companion Ear Tag, this file will contain a periodic measurement of the Bluetooth signal strength to the tag while it is connected. The RSSI is measured in dBm, and if a measurement is not yet available it will be logged at 127. The RSSI is logged at a 1 second interval while the companion ear tag is connected.
time,type,val,rssi
2025-01-23T04:33:38.480102Z,0,0x60fcf10031da,127
2025-01-23T04:33:39.481536Z,0,0x60fcf10031da,-85
2025-01-23T04:33:40.482971Z,0,0x60fcf10031da,-84
2025-01-23T04:33:41.484405Z,0,0x60fcf10031da,-84
Companion Ear Tag Logged Data
While a Bluetooth connection to a paired Companion Ear Tag is active, the Tauro research collar will log all data received over the Bluetooth link to the SD card. Files containing this data can be identified from the additional ID in the filename, for example infuse_{id_collar}_{id_device}_ACC_4G.csv, the {id_device} is the unique identifier of the Companion Ear Tag device.
1. Accelerometer Data {infuse_{id_collar}_{id_device}_ACC_4G.csv}
Raw accelerometer samples from a 12-bit 3-axis accelerometer. The accelerometer in the Companion Ear Tag samples at 50Hz, giving an expected period between samples of approximately 20 milliseconds (or 20000 microseconds).
time,x,y,z
2025-01-22T21:04:45.614044Z,208,-288,7888
2025-01-22T21:04:45.634033Z,192,-288,7888
2025-01-22T21:04:45.654022Z,208,-272,7888
2025-01-22T21:04:45.674011Z,192,-272,7888
The data is recorded in its raw format directly from the accelerometer, not converted into G’s in order to preserve maximum resolution. A maximum value of 16384 corresponding to an acceleration of +4G on that axis. As an example, converting the raw value of 7888 from the Z axis in the first row of the sample.
acceleration_g = 4 * 7888 / 16384
= 1.928
Conclusion
This document has provided an overview of the various data files generated by the Tauro Collar and their respective formats. Understanding these files is crucial for effective data analysis and interpretation of the information collected during deployments. For further details or assistance, please refer to the Tauro documentation or contact support.